![Phoenix Phamaceuticals/[Tyr0]-Adiponectin (17-41) (Human) - I-125 Labeled/10 µCi/T-028-49](images/PhoenixPhamaceuticals/aaexchange.png)
![Phoenix Phamaceuticals/[Tyr0]-Adiponectin (17-41) (Human) - I-125 Labeled/10 µCi/T-028-49](images/PhoenixPhamaceuticals/aaexchange.png)
 )
)Tyr-Asp-Gln-Glu-Thr-Thr-Thr-Gln-Gly-Pro-Gly-Val-Leu-Leu-Pro-Leu-Pro-Lys-Gly-Ala-Cys-Thr-Gly-Trp-Met-Ala |
- Radioactivity:
- Contents:
- Disclaimer:
| 10 µCi | |
| Each vial contains 10 µCi of Iodine-125 labeled peptide. | |
| This package conforms to the 49 CFR173.421 for expected radioactive material limited quantity, N.O.S. UN2910. |
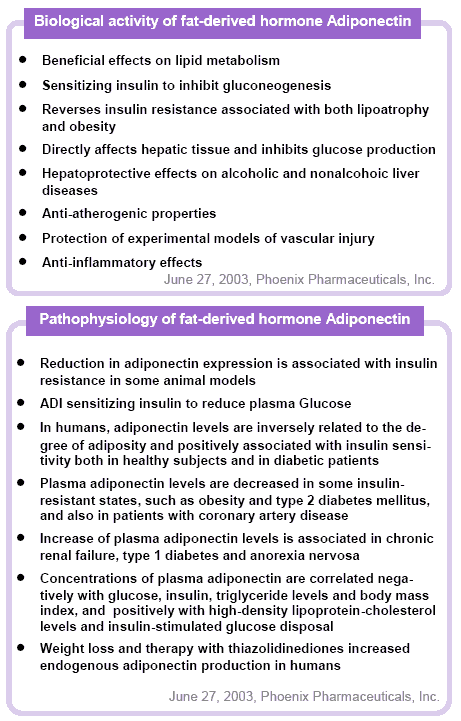
An Insulin-sensitizing adipocyte-derived hormone with central effects on energy homeostasis
- Abstracts
- Schematics
- More Information
  |  |
A collagen domain-derived short adiponectin peptide activates APPL1 and AMPK signaling pathways and improves glucose and fatty acid metabolisms.
Adiponectin is a fat tissue-derived adipokine with beneficial effects against diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. Accordingly, adiponectin-mimetic molecules possess significant pharmacological potential. Oligomeric states of adiponectin appear to determine its biological activity. We identified a highly conserved, 13-residue segment (ADP-1) from adiponectin"s collagen domain which comprises GXXG motifs and has one asparagine and two histidine residues that assist in oligomeric protein assembly. We therefore hypothesized that ADP-1 promotes oligomeric assembly and thereby mediates potential metabolic effects. We observed here that ADP-1 is stable in human serum and oligomerizes in aqueous environments. We also found that ADP-1 activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) in an adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interacting with PH domain and leucine zipper 1 (APPL1)-dependent pathway and stimulates glucose uptake in rat skeletal muscle cells (L-6 myotubes). ADP-1-induced glucose transport coincided with ADP-1-induced biosynthesis of glucose transporter 4 and its translocation to the plasma membrane. ADP-1 induced an interaction between APPL1 and the small GTPase Rab5 resulting in AMPK phosphorylation, in turn leading to phosphorylation of p38MAP kinase, acetyl coenzyme-A carboxylase, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. Similar to adiponectin, ADP-1 increased the expression of the adiponectin receptor 1 gene. Of note, ADP-1 decreased blood glucose levels and enhanced insulin production in pancreatic β cells in db/db mice. Further, ADP-1 beneficially affected lipid metabolism by enhancing lipid globule formation in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes. To our knowledge this is the first report on identification of a short peptidefrom adiponectin with positive effects on glucose or fatty acid metabolism.Sayeed M, Gautam S, Verma DP, et al. A collagen domain-derived short adiponectin peptide activates APPL1 and AMPK signaling pathways and improves glucose and fatty acid metabolisms. J Biol Chem. 2018;
Discovery of a novel potent peptide agonist to adiponectin receptor 1.
Activation of adiponectin receptors (AdipoRs) by its natural ligand, adiponectin has been known to be involved in modulating critical metabolic processes such as glucose metabolism and fatty acid oxidation as demonstrated by a number of in vitro and in vivo studies over last two decades. These findings suggest that AdipoRs" agonists could be developed into a potential therapeutic agent for metabolic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, especially for type II diabetes, a long-term metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Because of limitations in production of biologically active adiponectin, adiponectin-mimetic AdipoRs" agonists have been suggested as alternative ways to expand the opportunity to develop anti-diabetic agents. Based on crystal structure of AdipoR1, we designed AdipoR1"s peptide agonists using protein-peptide docking simulation and screened their receptor binding abilities and biological functions via surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and biological analysis. Three candidate peptides, BHD1028, BHD43, and BHD44 were selected and confirmed to activate AdipoR1-mediated signal pathways. In order to enhance the stability and solubility of peptide agonists, candidate peptides were PEGylated. PEGylated BHD1028 exhibited its biological activity at nano-molar concentration and could be a potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of diabetes. Also, SPR and virtual screening techniques utilized in this study may potentially be applied to other peptide-drug screening processes against membrane receptor proteins.Kim S, Lee Y, Kim JW, et al. Discovery of a novel potent peptide agonist to adiponectin receptor 1. PLoS ONE. 2018;13(6):e0199256.
A potent peptide as adiponectin receptor 1 agonist to against fibrosis.
Fibrotic diseases have become a major cause of death in the developed world. AdipoR1 agonists are potent inhibitors of fibrotic responses. Here, we focused on the in silico identification of novel AdipoR1 peptide agonists. A homology model was constructed to predict the 3D structure of AdipoR1. By docking to known active peptides, the putative active site of the model was further explored. A virtual screening study was then carried out with a set of manually designed peptides using molecular docking. Peptides with high docking scores were then evaluated for their anti-fibrotic properties. The data indicated that the novel peptide Pep70 significantly inhibited the proliferation of hepatic stellate cells (HSC) and NIH-3T3 cells (18.33% and 27.80%) and resulted in favouring cell-cycle arrest through increasing the accumulation of cells in the G0/G1 phase by 17.08% and 15.86%, thereby reducing the cell population in the G2/M phase by 11.25% and 15.95%, respectively. Additionally, Pep70 exhibited the most marked suppression on the expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), collagen type I alpha1 (COL1A1) and TGF-β1. Therefore, the peptide Pep70 was ultimately identified as an inhibitor of fibrotic responses and as a potential AdipoR1 agonist.Ma L, Zhang Z, Xue X, Wan Y, Ye B, Lin K. A potent peptide as adiponectin receptor 1 agonist to against fibrosis. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2017;32(1):624-631.
Design and development of a peptide-based adiponectin receptor agonist for cancer treatment.
BACKGROUND: Adiponectin, a fat tissue-derived adipokine, exhibits beneficial effects against insulin resistance, cardiovascular disease, inflammatory conditions, and cancer. Circulating adiponectin levels are decreased in obese individuals, and this feature correlates with increased risk of developing several metabolic, immunological and neoplastic diseases. Thus, pharmacological replacement of adiponectinmight prove clinically beneficial, especially for the obese patient population. At present, adiponectin-based therapeutics are not available, partly due to yet unclear structure/function relationships of the cytokine and difficulties in converting the full size adiponectin protein into a viable drug.RESULTS: We aimed to generate adiponectin-based short peptide that can mimic adiponectin action and be suitable for preclinical and clinical development as a cancer therapeutic. Using a panel of 66 overlapping 10 amino acid-long peptides covering the entire adiponectinglobular domain (residues 105-254), we identified the 149-166 region as the adiponectin active site. Three-dimensional modeling of the active site and functional screening of additional 330 peptide analogs covering this region resulted in the development of a lead peptidomimetic, ADP 355 (H-DAsn-Ile-Pro-Nva-Leu-Tyr-DSer-Phe-Ala-DSer-NH2). In several adiponectin receptor-positive cancer cell lines, ADP 355 restricted proliferation in a dose-dependent manner at 100 nM-10 μM concentrations (exceeding the effects of 50 ng/mL globular adiponectin). Furthermore, ADP 355 modulated several key signaling pathways (AMPK, Akt, STAT3, ERK1/2) in an adiponectin-like manner. siRNA knockdown experiments suggested that ADP 355 effects can be transmitted through both adiponectin receptors, with a greater contribution of AdipoR1. In vivo, intraperitoneal administration of 1 mg/kg/day ADP 355 for 28 days suppressed the growth of orthotopic human breast cancer xenografts by ~31%. The peptide displayed excellent stability (at least 30 min) in mouse blood or serum and did not induce gross toxic effects at 5-50 mg/kg bolus doses in normal CBA/J mice.CONCLUSIONS: ADP 355 is a first-in-class adiponectin receptor agonist. Its biological activity, superior stability in biological fluids as well as acceptable toxicity profile indicate that the peptidomimetic represents a true lead compound for pharmaceutical development to replace low adiponectin levels in cancer and other malignancies.Otvos L, Haspinger E, La russa F, et al. Design and development of a peptide-based adiponectin receptor agonist for cancer treatment. BMC Biotechnol. 2011;11:90
Adiponectin acts in the brain to decrease body weight.
Adiponectin (ADP) is an adipocyte hormone involved in glucose and lipid metabolism. We detected a rise in ADP in cerebrospinal fluid after intravenous (i.v.) injection, consistent with brain transport. In contrast to leptin, intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) administration of ADP decreased body weight mainly by stimulating energy expenditure. Full-length ADP, mutant ADP with Cys39 replaced with serine, and globular ADP were effective, whereas the collagenous tail fragment was not. Lep ob/ob mice were especially sensitive to i.c.v. and systemic ADP, which resulted in increased thermogenesis, weight loss and reduction in serum glucose and lipid levels. ADP also potentiated the effect of leptin on thermogenesis and lipid levels. While both hormones increased expression of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), ADP had no substantial effect on other neuropeptide targets of leptin. In addition, ADP induced distinct Fos immunoreactivity. Agouti (A y/a) mice did not respond to ADP or leptin, indicating the melanocortin pathway may be a common target. These results show that ADP has unique central effects on energy homeostasis.Qi Y, Takahashi N, Hileman SM, et al. Adiponectin acts in the brain to decrease body weight. Nat Med. 2004;10(5):524-9.
Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects.
Adiponectin (also known as 30-kDa adipocyte complement-related protein; Acrp30) is a hormone secreted by adipocytes that acts as an antidiabetic and anti-atherogenic adipokine. Levels of adiponectin in the blood are decreased under conditions of obesity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Administration of adiponectin causes glucose-lowering effects and ameliorates insulin resistance in mice. Conversely, adiponectin-deficient mice exhibit insulin resistance and diabetes. This insulin-sensitizing effect of adiponectin seems to be mediated by an increase in fatty-acid oxidation through activation of AMP kinase and PPAR-alpha. Here we report the cloning of complementary DNAs encoding adiponectin receptors 1 and 2 (AdipoR1 and AdipoR2) by expression cloning. AdipoR1 is abundantly expressed in skeletal muscle, whereas AdipoR2 is predominantly expressed in the liver. These two adiponectin receptors are predicted to contain seven transmembrane domains, but to be structurally and functionally distinct from G-protein-coupled receptors. Expression of AdipoR1/R2 or suppression of AdipoR1/R2 expression by small-interfering RNA supports our conclusion that they serve as receptors for globular and full-length adiponectin, and that they mediate increased AMP kinase and PPAR-alpha ligand activities, as well as fatty-acid oxidation and glucose uptake by adiponectin.Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Ito Y, et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature. 2003;423(6941):762-9.
Plasma adiponectin increases postprandially in obese, but not in lean, subjects.
We investigated the acute responses of plasma adiponectin levels to a test meal in lean and obese subjects. RESEARCH METHODS AND PROCEDURES: We studied 13 lean and 11 obese subjects after a 10-hour overnight fast. Glucose, insulin, and adiponectin concentrations were measured at baseline and 15, 30, 60, 120, and 180 minutes after a fixed breakfast. RESULTS: At baseline, fasting adiponectin concentrations were lower in the obese group vs. the lean group [mean (95% confidence interval): 2.9 (2.1 to 4.1) microg/mL vs. 8.6 (6.5 to 11.3) microg/mL], but rose 4-fold postprandially in the obese group, reaching a peak at 60 minutes [baseline: 2.9 (2.1 to 4.1) microg/mL vs. 60 minutes: 12.1 (8.5 to 17.4) microg/mL; p< 0.0001] and remaining elevated for the remainder of the study. There were no postprandial changes in plasma adiponectin concentrations in lean subjects. DISCUSSION: This increase of adiponectin concentrations in obese individuals might have important beneficial effects on postprandial glucose and lipid metabolism and might be viewed as a mechanism for maintaining normal glucose tolerance in those who are obese and insulin resistant.English PJ, Coughlin SR, Hayden K, Malik IA, Wilding JP. Plasma adiponectin increases postprandially in obese, but not in lean, subjects. Obes Res. 2003;11(7):839-44.
Ghrelin and adipose tissue regulatory peptides: effect of gastric bypass surgery in obese humans.
Presently surgery is the most effective way to obtain a controlled weight reduction in morbidly obese patients. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGBP) surgery is effective and used worldwide, but the exact mechanism of action is unknown. The effect of RYGBP on ghrelin, insulin, adiponectin, and leptin levels was investigated in 66 obese subjects; mean weight 127 kg (range, 96-195 kg) and mean body mass index (BMI) 45 kg/m(2) (range, 33-64) before and after surgery. Ghrelin levels were also compared in 10 nonoperated and 10 operated obese, BMI-matched women. RYGBP resulted in 22% and 30% weight loss at 6 and 12 months, respectively. Ghrelin increased by 44% and 62% and adiponectin by 36% and 98%, but insulin declined by 57% and 62% and leptin by 60% and 64%. The changes were all related to the reduction in BMI. In addition, ghrelin and insulin were inversely correlated at all time points as were changes of the peptides at 12 months (F = 4.9, P = 0.031), independent of the change in BMI. No evidence for RYGBP surgery per se having an effect on ghrelin levels, independent of weight loss, was obtained. The profound changes in the regulatory peptides are likely to reflect the new state of energy balance achieved. A close inverse association between ghrelin and insulin was observed, supporting an important role for ghrelin in glucose homeostasis.Holdstock C, Engström BE, Ohrvall M, Lind L, Sundbom M, Karlsson FA. Ghrelin and adipose tissue regulatory peptides: effect of gastric bypass surgery in obese humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88(7):3177-83.
The fat-derived hormone adiponectin alleviates alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases in mice.
Adiponectin has recently been shown to be a promising candidate for the treatment of obesity-associated metabolic syndromes. Replenishment of recombinant adiponectin in mice can decrease hyperglycemia, reverse insulin resistance, and cause sustained weight loss without affecting food intake. Here we report its potential roles in alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases in mice. Circulating concentrations of adiponectin decreased significantly following chronic consumption of high-fat ethanol-containing food. Delivery of recombinant adiponectin into these mice dramatically alleviated hepatomegaly and steatosis (fatty liver) and also significantly attenuated inflammation and the elevated levels of serum alanine aminotransferase. These therapeutic effects resulted partly from the ability of adiponectin to increase carnitine palmitoyltransferase I activity and enhance hepatic fatty acid oxidation, while it decreased the activities of two key enzymes involved in fatty acid synthesis, including acetyl-CoA carboxylase and fatty acid synthase. Furthermore, adiponectin treatment could suppress the hepatic production of TNF-alpha and plasma concentrations of this proinflammatory cytokine. Adiponectin was also effective in ameliorating hepatomegaly, steatosis, and alanine aminotransferase abnormality associated with nonalcoholic obese, ob/ob mice. These results demonstrate a novel mechanism of adiponectin action and suggest a potential clinical application of adiponectin and its agonists in the treatment of liver diseases.Xu A, Wang Y, Keshaw H, Xu LY, Lam KS, Cooper GJ. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin alleviates alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases in mice. J Clin Invest. 2003;112(1):91-100.
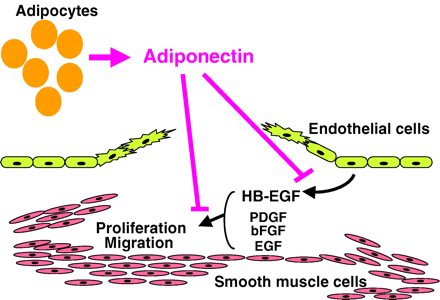
Role of adiponectin in preventing vascular stenosis. The missing link of adipo-vascular axis.
Obesity is more linked to vascular disease, including atherosclerosis and restenotic change, after balloon angioplasty. The precise mechanism linking obesity and vascular disease is still unclear. Previously we have demonstrated that the plasma levels of adiponectin, an adipose-derived hormone, decreases in obese subjects, and that hypoadiponectinemia is associated to ischemic heart disease. In current the study, we investigated the in vivo role of adiponectin on the neointimal thickening after artery injury using adiponectin-deficient mice and adiponectin-producing adenovirus. Adiponectin-deficient mice showed severe neointimal thickening and increased proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells in mechanically injured arteries. Adenovirus-mediated supplement of adiponectin attenuated neointimal proliferation. In cultured smooth muscle cells, adiponectin attenuated DNA synthesis induced by growth factors including platelet-derived growth factor, heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like growth factor (HB-EGF), basic fibroblast growth factor, and EGF and cell proliferation and migration induced by HB-EGF. In cultured endothelial cells, adiponectin attenuated HB-EGF expression stimulated by tumor necrosis factor alpha. The current study suggests an adipo-vascular axis, a direct link between fat and artery. A therapeutic strategy to increase plasma adiponectin should be useful in preventing vascular restenosis after angioplasty.
Matsuda M, Shimomura I, Sata M, et al. Role of adiponectin in preventing vascular stenosis. The missing link of adipo-vascular axis. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(40):37487-91.
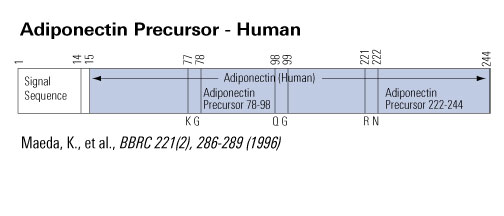
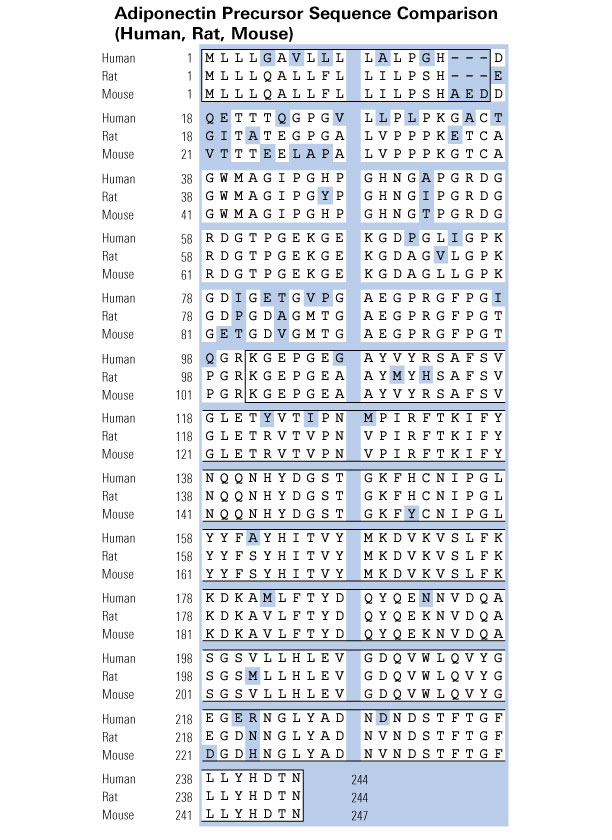
Hydroxylation and glycosylation of the four conserved lysine residues in the collagenous domain of adiponectin. Potential role in the modulation of its insulin-sensitizing activity.
It has recently been shown that the fat-derived hormone adiponectin has the ability to decrease hyperglycemia and to reverse insulin resistance. However, bacterially produced full-length adiponectin is functionally inactive. Here, we show that endogenous adiponectin secreted by adipocytes is post-translationally modified into eight different isoforms, as shown by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Carbohydrate detection revealed that six of the adiponectin isoforms are glycosylated. The glycosylation sites were mapped to several lysines (residues 68, 71, 80, and 104) located in the collagenous domain of adiponectin, each having the surrounding motif of GXKGE(D). These four lysines were found to be hydroxylated and subsequently glycosylated. The glycosides attached to each of these four hydroxylated lysines are possibly glucosylgalactosyl groups. Functional analysis revealed that full-length adiponectin produced by mammalian cells is much more potent than bacterially generated adiponectin in enhancing the ability of subphysiological concentrations of insulin to inhibit gluconeogenesis in primary rat hepatocytes, whereas this insulin-sensitizing ability was significantly attenuated when the four glycosylated lysines were substituted with arginines. These results indicate that full-length adiponectin produced by mammalian cells is functionally active as an insulin sensitizer and that hydroxylation and glycosylation of the four lysines in the collagenous domain might contribute to this activity.Wang Y, Xu A, Knight C, Xu LY, Cooper GJ. Hydroxylation and glycosylation of the four conserved lysine residues in the collagenous domain of adiponectin. Potential role in the modulation of its insulin-sensitizing activity. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(22):19521-9.
A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance.
Upper panel, inhibition of hepatic glucose production following treatment with increasing amounts of insulin in the absence or presence of 20µg/ml adiponectin (Ad) or Lys-to-Arg adiponectin variant (Ad variant) generated from COS-7 cells or 20µg/ml bacterially produced adiponectin (pAd); lower panel, inhibition of hepatic glucose production following treatment with 50 pM insulin plus increasing amounts of adiponectin or the Lys-to-Arg adiponectin variant generated from COS-7 cells or bacterially produced adiponectin. The results are represented as decreased percentage of glucose production relative to the untreated cells and as means S.D. (n = 4). Adipose tissue can have a substantial impact on systemic glucose homeostasis through production of bioactive molecules. We examined serum concentrations of adipocyte-derived secreted proteins with postulated roles in obesity and insulin action. ACRP30 (30-kDa adipocyte complement-related protein)/adiponectin concentrations in the obese Jnk1 -/- mice were significantly higher than in Jnk1 +/+ controls (Fig. 2e). In contrast, the concentrations of resistin were lower in Jnk1 -/- mice than in Jnk1 +/+ animals (Fig. 2f). Because recent studies have indicated a role for adiponectin as a mediator of fatty-acid oxidation and hepatic insulin sensitivity and resistin is postulated to have a role in insulin resistance, these alterations could affect systemic insulin sensitivity.Hirosumi J, Tuncman G, Chang L, et al. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature. 2002;420(6913):333-6.
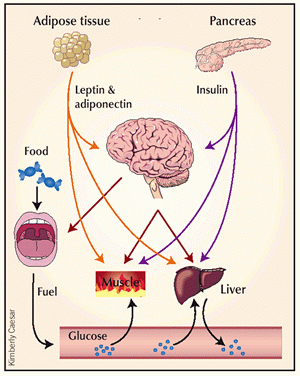
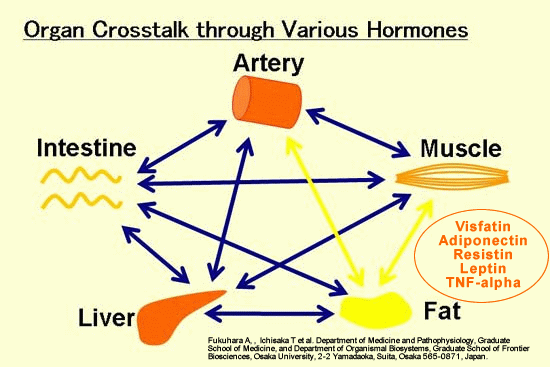
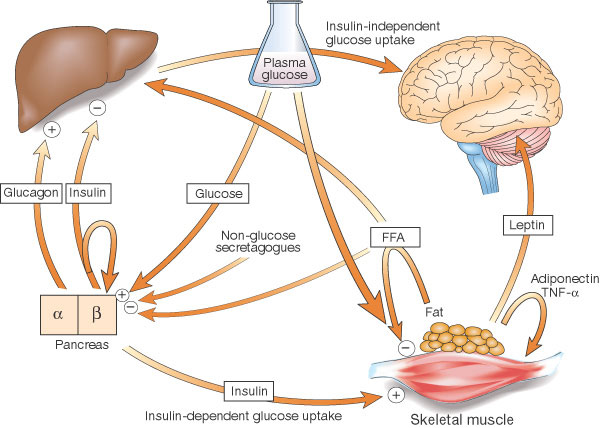 | Cross-talk between tissues in the regulation of glucose metabolism. Insulin is secreted from the alpha-cells of the pancreas in response to elevations in plasma glucose. The hormone decreases glucose production from the liver, and increases glucose uptake, utilization and storage in fat and muscle. The fat cell is important in metabolic regulation, releasing FFAs that reduce glucose uptake in muscle, insulin secretion from the alpha-cell, and increase glucose production from the liver. The fat cell can also secrete "adipokines" such as leptin, adiponectin and TNF, which regulate food intake, energy expenditure and insulin sensitivity. |
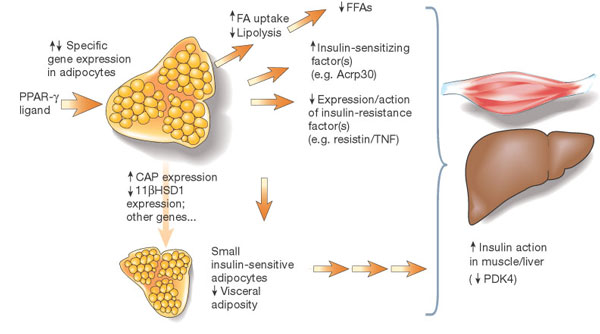 | Potential mechanisms of insulin sensitization by PPAR-alpha ligand"s. The receptor PPAR-alpha is predominantly expressed in adipose tissue. Ligand interactions with the receptor mediate specific changes in adipose gene expression. Altered expression of adipose genes such as fatty-acid transporter 1 may contribute to reduced production of free fatty acids (FFAs), which, in turn, is predicted to have insulin-sensitizing effects in muscle and liver. Changes in expression of other genes such as CAP or 11-alpha HSD1 may contribute to locally increased insulin action in adipose tissue and/or reduced visceral adiposity. Altered expression of circulating factors including TNF-Alpha, resistin and Acrp30 is also likely to indirectly mediate increased action of insulin in liver or muscle and glucose utilization; suppression of PDK4 activity in muscle is an example of one (probably indirect) effect. |
No References
hoenix Phamaceuticals
美国Phoenix药物集团创建于1994年,被誉为在多肽领域的黄金招牌,是这个领域的先行者和权威。
Phoenix Pharmaceuticals,Inc.专门提供肽和肽产品。我们提供肽抗体,荧光肽和放射性肽。我们在肽化学和有机合成领域拥有专业知识。
产品列表:
没有。 | 品牌 | 货号 | 名称 | 规格 |
1 | 凤凰药业 | |||
2 | 凤凰药业 | |||
3 | 凤凰药业 | |||
4 | 凤凰药业 | |||
5 | 凤凰药业 | 甲状腺素(T4)(人类)-ELISA试剂盒 |




本网站将在规定时间内给予删除等相关处理。